Understanding Fatty Liver: Causes, Symptoms, and Natural Support
Fatty liver disease is becoming increasingly common across the globe, silently impacting liver function and long-term health. This condition, often triggered by poor lifestyle choices or underlying medical issues, can lead to severe complications if not managed early. In this guide, we’ll explore the causes and symptoms of fatty liver disease and offer natural support strategies—highlighting Haional, a powerful supplement that supports liver health and overall wellness.
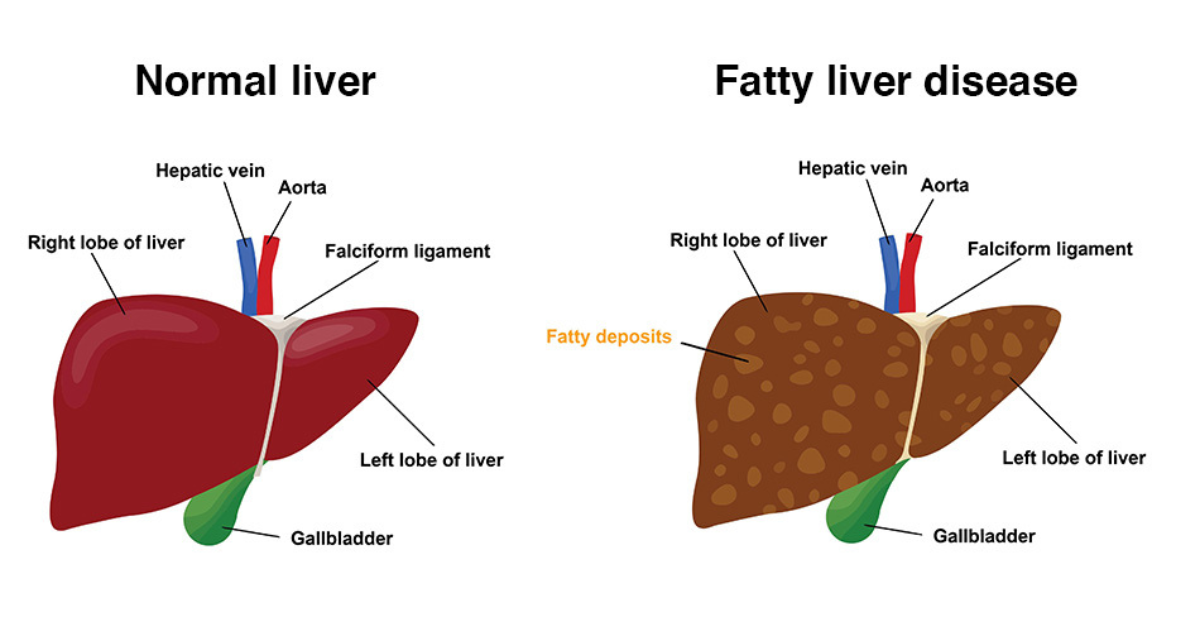
What Is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver cells, making up more than 5%–10% of the liver’s weight. Although having a small amount of fat in the liver is normal, too much can cause inflammation, impair liver function, and eventually lead to liver damage.
The Role of the Liver
The liver is one of the most vital organs in the body, responsible for over 500 functions, including:
-
Filtering toxins from the blood
-
Producing bile for digestion
-
Storing vitamins and minerals
-
Metabolizing nutrients and medications
-
Regulating blood sugar and cholesterol
When too much fat accumulates, it puts a strain on these essential processes. Over time, fatty liver can progress to more serious liver conditions.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two primary forms of fatty liver disease, and both can be equally dangerous if left unmanaged:
1. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
This is the most common type, especially in people who drink little to no alcohol. NAFLD is often linked with metabolic syndrome and is strongly associated with:
-
Obesity
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
High cholesterol or triglycerides
-
Insulin resistance
NAFLD can range from simple fatty liver (steatosis) to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), a more aggressive form that causes inflammation and liver cell damage, which may eventually lead to scarring (fibrosis) and cirrhosis.
2. Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD)
As the name suggests, ALD is caused by chronic and excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol is toxic to liver cells and triggers fat build-up, inflammation, and cell death. Continued alcohol intake despite early symptoms can cause the disease to progress to alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Stages of Fatty Liver Disease Progression
Fatty liver doesn't happen overnight—it develops in stages:
-
Simple Steatosis (Fat Accumulation)
The earliest stage with fat present but no significant inflammation or damage. -
Steatohepatitis (Fat + Inflammation)
Liver begins to show signs of irritation and inflammation. -
Fibrosis (Scarring)
Continued inflammation leads to the formation of scar tissue, replacing healthy liver tissue. -
Cirrhosis (Severe Scarring and Liver Failure)
Advanced stage where scar tissue permanently damages the liver, potentially leading to liver failure or liver cancer.
Why Early Detection Matters
Because fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic in its early stages, it frequently goes undiagnosed until liver function is already compromised. Early diagnosis through blood tests, imaging (ultrasound or CT scans), and sometimes a liver biopsy can make a big difference in reversing the condition.
Timely intervention—through diet, exercise, and natural liver support supplements like Haional—can significantly slow or even reverse the progression of fatty liver.
Common Causes of Fatty Liver
Understanding the root causes of fatty liver disease is essential for both prevention and treatment. This condition doesn't arise overnight; it's often the result of long-term lifestyle patterns, metabolic dysfunction, or underlying health conditions. Let's break down the most common fatty liver causes:
1. Unhealthy Diet and Poor Nutritional Habits
One of the leading contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a diet high in:
-
Refined carbohydrates (white bread, pastries, sugary cereals)
-
Added sugars (sodas, candies, desserts)
-
Trans fats and saturated fats (fried foods, processed meats, fast food)
These foods overload the liver with fat and sugar, especially fructose, which is metabolized directly in the liver and converted into fat. Over time, this can lead to insulin resistance, increased triglycerides, and fat accumulation in the liver cells.
Tip: A liver-friendly diet includes leafy greens, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, and antioxidant-rich fruits like berries and citrus.
2. Obesity and Excess Body Fat
Being overweight, particularly around the abdominal area, is strongly linked to fatty liver. Visceral fat—the fat stored around your organs—is metabolically active and increases free fatty acids in the blood, which the liver absorbs and stores.
-
Studies show that more than 70% of obese individuals have NAFLD.
-
The risk is even higher in those with central obesity (belly fat), even if their overall body weight is normal.
Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy body mass index (BMI) are essential strategies to prevent fatty liver.
3. Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin resistance, often seen in pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes, is a key driver of fatty liver disease. When cells become resistant to insulin:
-
Glucose builds up in the bloodstream
-
The pancreas produces more insulin
-
Excess glucose is stored as fat in the liver
This process creates a vicious cycle, as liver fat further worsens insulin resistance. As a result, individuals with type 2 diabetes have a significantly higher risk of developing NAFLD and its more severe form, NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis).
4. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) develops when the liver can no longer break down alcohol effectively, leading to fat accumulation, inflammation, and eventually fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Even moderate but regular alcohol intake can increase the liver’s workload and oxidative stress. The risk is compounded in individuals who already have other fatty liver risk factors, such as obesity or poor diet.
Important Note: Women tend to be more sensitive to alcohol-related liver damage than men, even at lower consumption levels.
5. High Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels
Elevated levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides contribute to fatty deposits in the liver. Dyslipidemia (abnormal fat levels in the blood) is frequently seen in people with fatty liver and is closely linked to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
Managing lipid profiles through diet, exercise, and supplementation can reduce liver fat and improve liver enzyme levels.
6. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity not only contributes to weight gain but also increases insulin resistance and systemic inflammation—both of which drive fat accumulation in the liver.
-
Physical inactivity is a known independent risk factor for fatty liver, even in people with normal body weight.
-
Engaging in aerobic exercises, resistance training, or even daily brisk walks can help reduce liver fat over time.
7. Certain Medications and Toxins
Some prescription drugs and environmental toxins can lead to drug-induced fatty liver. These include:
-
Methotrexate (used for cancer or autoimmune diseases)
-
Tamoxifen (used in breast cancer treatment)
-
Amiodarone (used for heart rhythm disorders)
-
Tetracycline antibiotics
8. Hormonal Imbalances and PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common hormonal disorder in women, is associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of fatty liver. Low levels of estrogen, especially after menopause, may also play a role in increasing liver fat accumulation in women.
9. Genetics and Family History
While lifestyle plays the most significant role, genetic factors can influence your risk. Some people are genetically predisposed to storing fat in their liver even if they maintain a healthy weight. Variants like PNPLA3 have been identified as increasing susceptibility to NAFLD.
If you have a family history of liver disease, diabetes, or obesity, it’s crucial to monitor your liver health closely.
10. Sleep Disorders and Stress
Emerging research links sleep apnea, chronic stress, and poor sleep quality to liver fat accumulation. These conditions disrupt the hormonal balance and metabolic processes, increasing the risk of NAFLD.
Practicing stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and prioritizing quality sleep may play a role in maintaining liver health.
Signs and Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
One of the most challenging aspects of fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis) is that it often progresses silently. Many people remain unaware they have liver fat accumulation until the condition is detected during routine checkups or imaging tests. However, as the disease progresses, certain signs and symptoms may start to appear, indicating the liver is under stress.
Recognizing these early signs of fatty liver can lead to timely intervention and lifestyle changes that may halt or reverse the condition.
1. Fatigue and Low Energy Levels
One of the earliest and most commonly reported symptoms is persistent fatigue or feeling unusually tired despite getting adequate rest. This occurs because the liver is working overtime to process excess fat, detoxify the body, and perform other metabolic functions. A sluggish liver means your body may not be processing nutrients and toxins efficiently, leading to an overall lack of energy.
2. Discomfort or Pain in the Upper Right Abdomen
A dull ache or discomfort in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, where the liver is located, is another possible sign of fatty liver. This may be due to liver enlargement (hepatomegaly) as fat continues to accumulate. The discomfort may be intermittent or constant and may worsen after eating fatty meals.
3. Unexplained Weight Gain or Difficulty Losing Weight
Because fatty liver disease is closely associated with insulin resistance, it can disrupt normal fat metabolism and contribute to:
-
Unexplained weight gain, particularly in the belly area
-
Difficulty losing weight despite diet and exercise
This weight-related resistance may also indicate metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that includes high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels—all risk factors for fatty liver.
4. Elevated Liver Enzymes
Often detected through routine blood tests, elevated levels of liver enzymes—such as ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase)—can be an early sign of liver inflammation or injury.
These tests are part of a liver function test (LFT) panel and may indicate that liver cells are leaking enzymes due to damage. However, some people with fatty liver have normal enzyme levels, which is why imaging and other diagnostics are also important.
5. Bloating and Digestive Issues
As the liver becomes compromised, it may impact digestion. Common symptoms include:
-
Bloating
-
Indigestion
-
Flatulence
-
Changes in bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea)
These symptoms can be subtle but often worsen after consuming high-fat or heavy meals.
6. Mental Fog and Poor Concentration (Hepatic Encephalopathy in Advanced Cases)
Although rare in early stages, as fatty liver disease progresses, liver dysfunction may impact brain function. This can lead to:
-
Difficulty concentrating
-
Forgetfulness
-
Confusion or mood swings
In severe cases (such as cirrhosis), toxins build up in the bloodstream and affect the brain, leading to a condition called hepatic encephalopathy.
7. Yellowing of the Skin or Eyes (Jaundice)
In advanced cases of fatty liver—especially when it has progressed to cirrhosis—you may notice:
-
Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
-
Dark-colored urine
-
Pale or clay-colored stools
These are classic symptoms of jaundice, indicating that the liver is failing to properly process bilirubin, a yellow pigment formed by the breakdown of red blood cells.
8. Swelling in Legs and Abdomen (Edema and Ascites)
Liver damage can also disrupt fluid regulation in the body. As a result, some individuals with advanced fatty liver may develop:
-
Swelling in the legs or ankles (edema)
-
Fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites)
This occurs when liver function deteriorates to the point that it affects protein synthesis and blood pressure regulation.
9. Skin Changes
Liver dysfunction can also manifest through the skin. Watch out for:
-
Dark patches on the neck or underarms (a condition called acanthosis nigricans, often seen in insulin resistance)
-
Spider angiomas – small, spider-like blood vessels visible under the skin
-
Red palms or itchy skin due to toxin buildup
10. Hormonal Imbalances
In both men and women, fatty liver disease can cause hormone-related changes such as:
-
Men: Reduced testosterone levels, loss of libido, or even breast enlargement (gynecomastia)
-
Women: Irregular menstrual cycles or worsened PCOS symptoms
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience a combination of the symptoms above—particularly abdominal discomfort, fatigue, and unexplained weight changes—consult your doctor for evaluation. Simple blood work and imaging tests (like ultrasound or CT scan) can help determine the extent of liver fat accumulation.
The good news? Fatty liver is reversible in most cases with proper diet, lifestyle adjustments, and natural liver-support supplements like Haional, which is specially formulated to aid in liver detox and fat metabolism.
Natural Remedies for Fatty Liver: Lifestyle & Nutrition Tips
When it comes to managing fatty liver disease, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in improving liver function, reducing fat accumulation, and preventing further damage. Fortunately, most individuals can take proactive steps to reverse fatty liver, especially in its early stages, without relying solely on medications.
Incorporating healthy habits, nutrition, and supplements can go a long way in reducing liver fat and supporting overall liver health. Below are some proven and effective natural remedies that can help manage and even reverse fatty liver disease.
1. Adopt a Healthy, Balanced Diet
A healthy diet is the foundation for managing fatty liver disease. Key dietary changes can reduce liver fat and inflammation, thereby promoting healing.
A. Focus on Whole Foods
Opt for whole, minimally processed foods that are rich in nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber. These foods promote liver health and improve fat metabolism. Some key foods to include are:
-
Leafy greens (spinach, kale, arugula)
-
Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts)
-
Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries) rich in antioxidants
-
Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds) for healthy fats and fiber
B. Include Healthy Fats
Contrary to popular belief, fats are essential for a healthy liver, but the right types of fats matter. Replace saturated and trans fats with:
-
Monounsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocado, and nuts
-
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are abundant in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds and chia seeds
These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties and support the reduction of fat in the liver.
C. Reduce Refined Carbohydrates and Sugar Intake
Refined carbohydrates and added sugars can worsen insulin resistance and contribute to fat buildup in the liver. Avoid:
-
White bread, pasta, and pastries
-
Sugary snacks and beverages
-
Processed foods with added sugars, such as sodas, sugary cereals, and candies
Instead, opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, which are high in fiber and have a lower glycemic index.
D. Increase Fiber Intake
A high-fiber diet helps support liver detoxification and can lower cholesterol levels. Include fiber-rich foods like:
-
Vegetables (such as sweet potatoes, carrots, and squash)
-
Fruits (like apples, pears, and citrus)
-
Legumes (lentils, beans, chickpeas)
-
Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, barley)
Fiber helps prevent fat accumulation in the liver and aids digestion by binding to toxins and removing them from the body.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight is a major contributor to fatty liver disease, particularly nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Losing just 5-10% of your body weight can significantly reduce liver fat and improve liver function. Healthy weight management can be achieved through:
-
Regular exercise: Engage in aerobic exercises such as walking, cycling, or swimming, which have been shown to reduce liver fat.
-
Strength training: Building muscle mass through resistance exercises can improve insulin sensitivity and metabolism.
-
Caloric reduction: Avoid extreme diets or fasting. Focus on gradual weight loss through a sustainable, calorie-controlled diet.
3. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration supports liver detoxification and helps in the processing and elimination of toxins. Water assists the liver in flushing out waste products and improving digestion. Drinking enough water can also reduce the risk of developing gallstones, which are often associated with fatty liver disease.
Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day, and limit sugary or high-calorie drinks such as sodas and juices that can contribute to weight gain.
5. Limit Alcohol Intake
Alcohol consumption is a well-known cause of liver damage, including alcoholic fatty liver disease. However, even in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), excessive alcohol intake can exacerbate liver fat accumulation and liver damage.
If you have fatty liver disease, it's important to:
-
Limit alcohol consumption or avoid it entirely to prevent further liver strain.
-
Speak to your healthcare provider about safe alcohol limits or abstaining from alcohol altogether for better liver health.
6. Herbal and Natural Supplements to Support Liver Health
Certain natural remedies and liver-supporting supplements can enhance liver function and aid in fatty liver management. Some of the most commonly used natural supplements include:
A. Milk Thistle (Silymarin)
Milk thistle is well known for its liver-protecting properties. It contains silymarin, a compound that:
-
Reduces liver inflammation
-
Supports liver cell regeneration
-
Protects against liver damage caused by toxins or free radicals
B. Turmeric (Curcumin)
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It may help:
-
Reduce liver inflammation
-
Prevent liver fibrosis (scarring)
-
Improve overall liver function
Adding turmeric to your meals or taking turmeric supplements may have long-term benefits for liver health.
C. Dandelion Root
Dandelion root is another herbal remedy that supports liver detoxification. It helps:
-
Stimulate bile production for better digestion
-
Promote the removal of toxins from the liver
-
Improve overall liver function and digestion
D. Haional Supplement for Liver Health
For a more direct and targeted approach, Haional is a specialized supplement formulated to support liver health and improve fat metabolism. Haional can:
-
Help detoxify the liver
-
Promote fat breakdown and reduce fat accumulation
-
Improve liver enzyme levels, particularly in individuals with fatty liver disease
Haional is designed to work synergistically with lifestyle changes and a liver-friendly diet to provide effective, long-term results. Incorporating Haional into your daily routine can enhance the benefits of dietary and lifestyle changes, helping you manage fatty liver effectively.
E. Artichoke Extract
Artichoke extract is a natural compound that supports liver detoxification and helps regenerate liver cells. Its benefits include:
-
Enhancing bile production, which aids in fat digestion and detoxification
-
Reducing liver fat and improving the body’s ability to metabolize fats
-
Supporting the liver's detoxification pathways, helping remove harmful substances from the body
Artichoke extract is an excellent choice for individuals dealing with fatty liver or those who want to improve digestion and liver detoxification.
7. Prioritize Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for overall health and wellness, including liver function. Chronic sleep deprivation can disrupt the body's metabolic processes and increase the risk of developing insulin resistance and fatty liver disease.
Ensure you are getting at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night, and practice good sleep hygiene by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, reducing screen time before bed, and creating a calm, dark sleep environment.
🛍️ Looking for More Natural Wellness Solutions?
Explore a wide range of natural dietary supplements in Pakistan on Jarrett Pharma’s Dietary Supplements Collection Page. Whether you’re managing liver health, improving digestion, or supporting joint function, Jarrett Pharma offers high-quality, research-backed products to elevate your daily wellness routine.
Holistic Health Tip: Joint Health and Liver Wellness Go Hand-in-Hand
Your body works as a system—and improving one area often enhances another. Inflammation, which can negatively affect the liver, also plays a significant role in joint degeneration.
If you’re already focusing on liver health, it’s worth paying attention to your joints as well. Learn more by exploring these helpful articles from our blog:
-
🔗 5 Early Signs of Joint Degeneration and How to Address Them
-
🔗 Hyaluronic Acid vs Glucosamine: Which is Better for Joint Pain?
These resources not only promote joint health but offer insight into reducing overall inflammation—benefiting your liver and beyond.
Final Thoughts: Start Reversing Fatty Liver Today
Fatty liver disease is more common than most people think—but it doesn't have to be a life sentence. By understanding the fatty liver causes and symptoms, and embracing natural remedies, you can take proactive steps toward better liver health.
Adding a trusted supplement like Haional to your wellness routine can amplify the benefits of lifestyle changes. Backed by natural ingredients and designed to support liver detox and function, it’s an ideal choice for anyone looking to live a cleaner, healthier life.
Ready to take charge of your liver health? Explore Haional today and discover the difference natural liver support can make.